Record Number
1166
PROSEA Handbook Number
12(2): Medicinal and poisonous plants 2
Taxon
Limnophila aromatica (Lamk) Merr.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Limnophila in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Limnophila in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
Protologue
Interpr. Herb. amboin.: 466 (1917).
Synonyms
Gratiola aromatica (Lamk) Pers. (1805), Limnophila punctata Blume (1826), Limnophila gratissima Blume (1826).
Vernacular Names
Indonesia: kehkehan (Sundanese), daun kardemom, selaseh ayer kecil (Ambonese). Malaysia: beremi, kerak-kerak. Philippines: angangi (Bontok). Papua New Guinea: poikehkeh (Wapi), ginibok (Keepaukee). Thailand: phak khayaeng (central), phak phaa (northern). Vietnam: rau ng[oom].
Distribution
From India and Sri Lanka to Indo-China, southern China, Japan, Taiwan, throughout South-East Asia and northern Australia.
Uses
In Indonesia and Peninsular Malaysia, the sap of the leaves is used to clean wounds, and a decoction of the leaves is given in fevers.
Observations
A variable, fleshy, annual to perennial herb, 30B-100 cm tall, stems simple or shortly branched from the base, glabrous to minutely glandular; leaves decussate or in whorls of 3, ovate-lanceolate to lanceolate, 10B-55 mm x 3-B15 mm, margins crenate to serrate-dentate, glabrous to densely and minutely glandular, pinnately veined, sessile; flowers solitary and axillary, or a few to many-flowered, terminal or axillary raceme, up to 15 cm long, pedicel 5B20 mm long, bracteoles 2, 1.5-B2 mm long, calyx 4.5B-7 mm long, hairy, striate at maturity, corolla 10.5B-13.5 mm long, pale pink, outside finely glandular, inside densely villous, posterior lobe emarginate, posterior stamens 2.5 mm long, villous, anterior stamens 4 mm long, glabrous; capsule broadly ellipsoid, compressed, 5—6 mm long, brown. Limnophila aromatica grows in shallow ponds or marshy localities, from sea-level up to 1000 m altitude. It is closely related to Limnophila chinensis (Osbeck) Merr., and some authors consider Limnophila aromatica as a subspecies of it.
Image
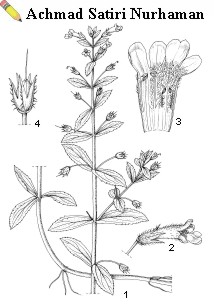 | Limnophila aromatica (Lamk) Merr. - 1, plant habit; 2, flower; 3, opened corolla with stamens; 4, fruit |
Selected Sources
[135] Burkill, I.H., 1966. A dictionary of the economic products of the Malay Peninsula. Revised reprint. 2 volumes. Ministry of Agriculture and Co-operatives, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Vol. 1 (A—H) pp. 1—1240, Vol. 2 (I—Z) pp. 1241—2444.
[407] Heyne, K., 1950. De nuttige planten van Indonesië [The useful plants of Indonesia]. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. W. van Hoeve, 's-Gravenhage, the Netherlands/Bandung, Indonesia. 1660 + CCXLI pp.
[747] Ochse, J.J. & Bakhuizen van den Brink, R.C., 1980. Vegetables of the Dutch East Indies. 3rd English edition (translation of "Indische groenten"", 1931). Asher & Co., Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1016 pp.
[810] Quisumbing, E., 1978. Medicinal plants of the Philippines. Katha Publishing Co., Quezon City, the Philippines. 1262 pp.
[837] Reddy, G.B.S., Melkhani, A.B., Kalyani, G.A., Rao, J.V., Shirwaikar, A., Aithal, K.S., Udupa, A.L., Srinivasan, K.K., Kotian, M., Ramani, R. & Bhat, G., 1991. Chemical and pharmacological investigations of Limnophila conferta and Limnophila heterophylla. International Journal of Pharmacognosy 29(2): 145—153.
[407] Heyne, K., 1950. De nuttige planten van Indonesië [The useful plants of Indonesia]. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. W. van Hoeve, 's-Gravenhage, the Netherlands/Bandung, Indonesia. 1660 + CCXLI pp.
[747] Ochse, J.J. & Bakhuizen van den Brink, R.C., 1980. Vegetables of the Dutch East Indies. 3rd English edition (translation of "Indische groenten"", 1931). Asher & Co., Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 1016 pp.
[810] Quisumbing, E., 1978. Medicinal plants of the Philippines. Katha Publishing Co., Quezon City, the Philippines. 1262 pp.
[837] Reddy, G.B.S., Melkhani, A.B., Kalyani, G.A., Rao, J.V., Shirwaikar, A., Aithal, K.S., Udupa, A.L., Srinivasan, K.K., Kotian, M., Ramani, R. & Bhat, G., 1991. Chemical and pharmacological investigations of Limnophila conferta and Limnophila heterophylla. International Journal of Pharmacognosy 29(2): 145—153.
Author(s)
G.H. Schmelzer
Correct Citation of this Article
Schmelzer, G.H., 2001. Limnophila aromatica (Lamk) Merr.. In: van Valkenburg, J.L.C.H. and Bunyapraphatsara, N. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 12(2): Medicinal and poisonous plants 2. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.