Record Number
1484
PROSEA Handbook Number
2: Edible fruits and nuts
Taxon
Carica papaya L.
Protologue
Sp. Pl.: 1036 (1753).
Family
CARICACEAE
Chromosome Numbers
2n = 18
Vernacular Names
Papaya, pawpaw, melon tree (En). Papayier, arbre de melon (Fr). Indonesia: papaya, gedang (Sundanese), kates (Javanese). Malaysia: papaya, betek, ketalah. Philippines: papaya, kapaya, lapaya. Burma: thimbaw. Cambodia: lhong, doeum lahong. Laos: houng. Thailand: malakor (central), loko (peninsular), ma kuai thet (northern). Vietnam: du du.
Origin and Geographic Distribution
The genus Carica L. is indigenous to tropical America and the papaya must have originated from natural hybridization involving Carica peltata Hook. & Arn. From tropical America it was brought to the Caribbean and South-East Asia during the Spanish exploration in the 16th Century. It then spread rapidly to India, Oceania, Africa, and today it is widely distributed throughout the tropical and warmer subtropical areas of the world.
Uses
Ripe papaya is a favourite breakfast and dessert fruit that is available year-round. It can be used to make fruit salads, refreshing drinks, jam, jelly, marmalade, candies and crystallized fruits. Green fruits are pickled or cooked as vegetable. In Java, a sweetmeat is made from the flowers. Young leaves are sometimes eaten. In some countries, seeds are used as vermifuge and abortifacient. Carpaine, an alkaloid present in papaya, can be used as a heart depressant, amoebicide and diuretic. In some countries papaya is grown in sizeable plantations for the extraction of papain, a proteolytic enzyme present in the latex, collected mainly from the green fruit. Papain has varied uses in the beverage, food and pharmaceutical industries: in chill-proofing beer, tenderizing meat, drug preparations for digestive ailments and treatment of gangrenous wounds. It is also used in bathing hides, degumming silk and softening wool.
Production and International Trade
FAO statistics for 1988 show a total world production of 3.68 million t. Among the major producers are Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, India and Zaire. In the same year Asia contributed nearly 25% of the total papaya production; within the region, Indonesia produced 270 000 t, the Philippines 95 000 t, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea 12 000 t each; no production data are available for Thailand. The Philippines exports a modest amount of fresh papaya to Hong Kong and New Zealand. Malaysia and Thailand export to Singapore.
The papaya fruit is delicate and perishable and therefore lags far behind banana and pineapple in world trade. Since so much of the fruit is grown in home gardens and does not reach beyond local markets, official statistics probably greatly underestimate the importance of the crop.
The papaya fruit is delicate and perishable and therefore lags far behind banana and pineapple in world trade. Since so much of the fruit is grown in home gardens and does not reach beyond local markets, official statistics probably greatly underestimate the importance of the crop.
Properties
About 60% of the ripe fruit is edible. The approximate contents per 100 g edible portion are: water 86.6 g, protein 0.5 g, fat 0.3 g, carbohydrates 12.1 g, fibre 0.7 g, ash 0.5 g, potassium 204 mg, calcium 34 mg, phosphorus 11 mg, iron 1 mg, sodium 3 mg, vitamin A 450 mg, vitamin C 74 mg, thiamine 0.03 mg, niacin 0.5 mg, and riboflavin 0.04 mg. The energy value is 200 kJ/100 g. Major sugars are sucrose (48.3%), glucose (29.8%) and fructose (21.9%).
Description
A fast-growing tree-like herb, 2—10 m tall, usually unbranched, sometimes branched due to injury, containing white latex in all parts. Stem cylindrical, 10—30 cm in diameter, hollow, with prominent leaf scars and spongy-fibrous tissue. Leaves spirally arranged, clustered near apex of trunk; petiole up to 1 m long, hollow, greenish or purplish-green; lamina orbicular, 25—75 cm in diameter, palmately and deeply 7—11-lobed, glabrous, prominently veined, lobes deeply and broadly toothed. Flowers male, female or hermaphrodite, axillary, found on separate trees. Male flowers in panicles, 25—100 cm long, pendent, sessile; calyx cup-shaped, small, 5-toothed; corolla trumpet-shaped, 2.5 cm long, with 5 spreading lobes, light yellow; stamens 10, in 2 whorls alternating with the petal lobes. Female flowers solitary or in few-flowered cymes, 3.5—5 cm long; calyx cup-shaped, 3—4 mm long, with 5 narrow teeth, yellow-green; corolla of 5 almost free petals; petals lanceolate, twisted, fleshy, yellow; ovary ovoid-oblong, 2—3 cm long, with central cavity and numerous ovules; stigmas 5, fan-shaped, sessile, deeply 5-cleft. Hermaphrodite flowers of 2 types: 'elongata' type with flowers in short-peduncled clusters, partially united petals, stamens 10 in 2 series, ovary elongate; 'pentandria' type, flowers similar to female flowers but with 5 stamens. Intermediate flowers occur as well, in which stamens become carpelloid producing irregular fruits. Proportion and type of flowers produced may vary on same tree, depending on age and environmental conditions. Fruit a fleshy berry, ovoid-oblong to nearly spherical, or pyriform, cylindrical or grooved, 7—30 cm long, weighing up to 10 kg; skin thin, smooth, yellowish or orange in ripe fruit; flesh yellowish to red-orange, edible, sweet with mild and pleasant flavour; central cavity 5-angled. Seeds globose, 5 mm in diameter, black or greyish, numerous, attached in 5 rows to interior wall of ovary, enclosed in a gelatinous sarcotesta.
Image
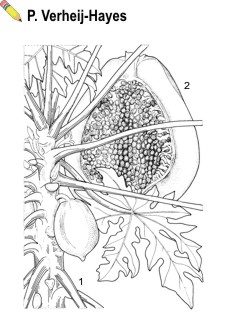 | Carica papaya L. - 1, part of flowering and fruiting stem; 2, halved fruit |
Growth and Development
Papaya is grown from seed. Germination is epigeal and takes 2—3 weeks. Seedlings grow rapidly. Since their sex cannot be determined before flowering, normal practice is to plant 3—5 seedlings together and retain only the most vigorous hermaphrodite or female plant at flowering. With controlled pollination, the ratios of female, hermaphrodite and male offspring are predictable:
— female x male —> 1 female : 1 male;
— female x hermaphrodite —> 1 female : 1 hermaphrodite;
— hermaphrodite x male —> 1 female : 1 hermaphrodite : 1 male.
Thus in some combinations all resulting plants should bear fruit. Pollination is basically by wind and aided by small insects like thrips.
Papaya trees may live up to 25 years or more but productivity declines with age. For fresh fruit production as well as papain production it is best to renew the plantation every 3 years. The life history of a plant can be read from the leaf scars: closely-spaced scars of reduced size betray a period of stress. When all is well, two leaves emerge each week. A high initial growth rate leads to early flowering (within 6 months from sowing) and fruiting (fruit maturing 4—5 months after flowering). The fruit moderates the growth rate, but a steady and relatively fast pace should be maintained to produce fruit throughout the year and in large quantity.
— female x male —> 1 female : 1 male;
— female x hermaphrodite —> 1 female : 1 hermaphrodite;
— hermaphrodite x male —> 1 female : 1 hermaphrodite : 1 male.
Thus in some combinations all resulting plants should bear fruit. Pollination is basically by wind and aided by small insects like thrips.
Papaya trees may live up to 25 years or more but productivity declines with age. For fresh fruit production as well as papain production it is best to renew the plantation every 3 years. The life history of a plant can be read from the leaf scars: closely-spaced scars of reduced size betray a period of stress. When all is well, two leaves emerge each week. A high initial growth rate leads to early flowering (within 6 months from sowing) and fruiting (fruit maturing 4—5 months after flowering). The fruit moderates the growth rate, but a steady and relatively fast pace should be maintained to produce fruit throughout the year and in large quantity.
Other Botanical Information
Because of outcrossing the plants do not produce true to type. There is much variation, not only in home-grown plants, but also between plants in an orchard. However, in Thailand hermaphrodites are used and in the absence of other pollen sources it is not difficult to develop and maintain cultivars (e.g. the long-fruited red-fleshed 'Kaeg-dahm' and the smaller yellowish 'Kaeg-nuan'). Note that even in this case there is genetic variability, since fruit from female plants is not the same as that from hermaphrodite plants.
In some places in South-East Asia the highly inbred hermaphrodite cultivars of the Solo group from Hawaii have come to the fore, e.g. 'Kapoho', 'Sunrise' and 'Sunset'. Where these introductions are surrounded by local material, much care is needed to maintain the cultivars. Agricultural research in Malaysia has yielded several cultivars, such as 'Subang', 'Sitiawan', 'Batu Arang', 'Kundang' and 'Eksotika' (the latter a Solo cultivar derived from a series of back-crosses involving 'Subang 6' and 'Sunrise'). 'Cavite' is a big-fruited selection in the Philippines. 'Coimbatore-2' and 'Peradeniya', both dioecious cultivars, are suitable for papain production.
In some places in South-East Asia the highly inbred hermaphrodite cultivars of the Solo group from Hawaii have come to the fore, e.g. 'Kapoho', 'Sunrise' and 'Sunset'. Where these introductions are surrounded by local material, much care is needed to maintain the cultivars. Agricultural research in Malaysia has yielded several cultivars, such as 'Subang', 'Sitiawan', 'Batu Arang', 'Kundang' and 'Eksotika' (the latter a Solo cultivar derived from a series of back-crosses involving 'Subang 6' and 'Sunrise'). 'Cavite' is a big-fruited selection in the Philippines. 'Coimbatore-2' and 'Peradeniya', both dioecious cultivars, are suitable for papain production.
Ecology
Papaya thrives in warm areas with adequate rainfall and a temperature range of 21—33°C. Its altitude range is similar to that of the banana, from sea level to elevations at which frosts occur (often around 1600 m). Frost can kill the plant, and cool and overcast weather delays fruit ripening and depresses fruit quality. Fruit tastes much better when grown during a warm sunny season, but yield can be very high at elevations around 1000 m, the altitude for papain production in East Africa in the 1960s. Evenly distributed annual rainfall of 1200 mm is sufficient if water conservation practices are employed. Plantations should be in sheltered locations or surrounded by windbreaks; strong winds are detrimental, particularly on soils which cannot make up for large transpiration losses.
Papaya grows best in light, well-drained soils rich in organic matter with soil pH of 6.0—6.5. It can tolerate any kind of soil provided it is well-drained and not too dry. The roots are very sensitive to waterlogging and even short periods of flooding can kill the plants.
Papaya grows best in light, well-drained soils rich in organic matter with soil pH of 6.0—6.5. It can tolerate any kind of soil provided it is well-drained and not too dry. The roots are very sensitive to waterlogging and even short periods of flooding can kill the plants.
Propagation and planting
Papaya is propagated by seed. Several techniques are known to produce cuttings but these are too laborious compared with the use of seedlings. To reproduce the desired characteristics it is best to get seeds through controlled pollination. The sarcotesta enveloping the seed is removed (because it inhibits germination) by rubbing the seed together against a fine-meshed screen under running water. Thoroughly dried seeds stored in air-tight containers remain viable for several years.
Seeds are sown in small containers (tin cans, plastic bags or paper cups) at the rate of 3—4 seeds per container. Use of sterilized soil minimizes losses resulting from nematodes and damping-off fungi. Germination takes 2—3 weeks. Another practice is to sow the seeds in sterilized nursery beds and to prick out at the 2—3-leaf stage, transferring 3—4 seedlings to each container. Seedlings are transplanted about 2 months after sowing when they reach the 3—4-leaf stage or 20 cm height, preferably at the onset of the rainy season. During transplanting, care should be exercised so as not to disturb the roots. Older seedlings recover poorly after planting out. Papaya needs adequate drainage and is often planted on mounds or ridges. Transplants must be watered regularly until they are established.
Field spacings are in the order of 3 m x 2 m to 2.50 m x 1.60 m, giving densities of 1667 and 2500 plants/ha respectively. The same densities are obtained by planting in double rows spaced (3.25 + 1.75) m x 2.40 m or (2.50 + 1.50) m x 2 m. Thinning to one female or one hermaphrodite plant per hill is done when the plants reach the flowering stage. In the absence of hermaphrodite plants, 1 male plant per 25—100 female plants is retained as pollinator.
Papaya grows best when planted in full sunlight. However, it can be planted as an intercrop under coconut as practised in the Philippines and other countries, or as a cash crop between young fruit trees such as mango, citrus or rambutan.
Seeds are sown in small containers (tin cans, plastic bags or paper cups) at the rate of 3—4 seeds per container. Use of sterilized soil minimizes losses resulting from nematodes and damping-off fungi. Germination takes 2—3 weeks. Another practice is to sow the seeds in sterilized nursery beds and to prick out at the 2—3-leaf stage, transferring 3—4 seedlings to each container. Seedlings are transplanted about 2 months after sowing when they reach the 3—4-leaf stage or 20 cm height, preferably at the onset of the rainy season. During transplanting, care should be exercised so as not to disturb the roots. Older seedlings recover poorly after planting out. Papaya needs adequate drainage and is often planted on mounds or ridges. Transplants must be watered regularly until they are established.
Field spacings are in the order of 3 m x 2 m to 2.50 m x 1.60 m, giving densities of 1667 and 2500 plants/ha respectively. The same densities are obtained by planting in double rows spaced (3.25 + 1.75) m x 2.40 m or (2.50 + 1.50) m x 2 m. Thinning to one female or one hermaphrodite plant per hill is done when the plants reach the flowering stage. In the absence of hermaphrodite plants, 1 male plant per 25—100 female plants is retained as pollinator.
Papaya grows best when planted in full sunlight. However, it can be planted as an intercrop under coconut as practised in the Philippines and other countries, or as a cash crop between young fruit trees such as mango, citrus or rambutan.
Husbandry
Clean cultivation is standard practice in South-East Asia. Weed control, particularly around the small plants, is very important. If weeds are only slashed — resulting in a grassy weed cover — the papaya plants suffer severe competition. Experimental work shows a very good response to mulching.
Irrigation is needed to minimize flower abortion and maintain growth during the dry season. Watering once a week is recommended if there are no data on crop water use, soil depth and moisture retention.
Papaya is a fast-growing crop that requires heavy fertilization. Nutrient removal is in the order of 1 kg N, 0.2 kg P and 2.5 kg K per tonne fruit. In addition substantial quantities of nutrients are tied up in the vegetative parts. The fertilizer should be split between 2—4 applications per year; use of manure and mulch steadies the release of nutrients. Calcium deficiency depresses growth and fruit set and enhances fruit drop; liming (to a pH of about 6) is the remedy. Fruit malformation, characterized by lumpiness or rough bumps on the fruit, has been associated with boron deficiency; 20—40 g borax per tree can alleviate the problem.
Irrigation is needed to minimize flower abortion and maintain growth during the dry season. Watering once a week is recommended if there are no data on crop water use, soil depth and moisture retention.
Papaya is a fast-growing crop that requires heavy fertilization. Nutrient removal is in the order of 1 kg N, 0.2 kg P and 2.5 kg K per tonne fruit. In addition substantial quantities of nutrients are tied up in the vegetative parts. The fertilizer should be split between 2—4 applications per year; use of manure and mulch steadies the release of nutrients. Calcium deficiency depresses growth and fruit set and enhances fruit drop; liming (to a pH of about 6) is the remedy. Fruit malformation, characterized by lumpiness or rough bumps on the fruit, has been associated with boron deficiency; 20—40 g borax per tree can alleviate the problem.
Diseases and Pests
Damping-off is caused by the soilborne fungi Phytophthora parasitica, P. palmivora and Pythium aphanidermatum. Phytophthora also occurs in the orchard, infecting both the trunk and the fruit. Good aeration, drainage, and hygiene are important to curb these fungi in the orchard as well as in the nursery. It is advisable not to replant papaya on the same land. Anthracnose, caused by Glomerella cingulata (imperfect form: Colletotrichum gloeosporioides), primarily infects the fruit. The disease appears as small water-soaked circular spots that enlarge into brown-black sunken lesions as the fruit ripens. Fungicidal spray at 7—10-day intervals can control this disease. A 20-minute hot water dip (45°C) reduces post-harvest decay.
Papaya ringspot is a devastating virus disease that was detected in the Philippines in 1982. It had earlier caused considerable losses in Hawaii, Florida and Taiwan. Initially, the disease appears as oil streaks on stems and petioles and as it progresses, mottling of leaves becomes evident. Severely infected plants do not flower and die young. The virus is transmitted by aphids. Control measures are planting in isolation, removing and destroying infected plants, and using tolerant cultivars. Cross-protection has been advocated, but this requires the availability of a mild virus strain for inoculation of seedlings. Mosaic is another virus disease transmitted by aphids, and bunchy top is caused by a mycoplasma transmitted by a hopper.
Rootknot (Meloidogyne incognita) and reniform (Rotylenchulus reniformis) nematodes infest papaya. Feeding nematodes cause root swellings or root galls, resulting in yellowing and premature abscission of the leaves. Since nematicide treatments are expensive, it is important to use clean land, not replanting papaya in the same field.
The oriental fruit fly (Dacus dorsalis) is a major concern of papaya- importing countries such as Japan and the United States. The flies deposit their eggs in ripe fruit. Fruit should be harvested at the mature green stage. Over-ripe and infested fruit should be buried. Male flies can be baited by placing a cotton ball dipped in methyl eugenol-malathion solution inside trap bottles positioned every 25 m throughout the plantation.
Mites (Tetranychus kansawai and Brevipalpus californicus) suck the plant sap, leading to poor plant growth and blemishes on the fruit. Predatory mites generally provide adequate control, an additional reason for restraint in the use of acaricides or insecticides with miticidal action. Aphid (Aphis gossypii, Myzus persicae) infestation weakens the plants and aphids also transmit virus diseases. Removing alternative hosts and the presence of natural predators can effectively reduce aphid populations. Spraying insecticide on the undersides of the leaves is also an effective control measure.
Papaya ringspot is a devastating virus disease that was detected in the Philippines in 1982. It had earlier caused considerable losses in Hawaii, Florida and Taiwan. Initially, the disease appears as oil streaks on stems and petioles and as it progresses, mottling of leaves becomes evident. Severely infected plants do not flower and die young. The virus is transmitted by aphids. Control measures are planting in isolation, removing and destroying infected plants, and using tolerant cultivars. Cross-protection has been advocated, but this requires the availability of a mild virus strain for inoculation of seedlings. Mosaic is another virus disease transmitted by aphids, and bunchy top is caused by a mycoplasma transmitted by a hopper.
Rootknot (Meloidogyne incognita) and reniform (Rotylenchulus reniformis) nematodes infest papaya. Feeding nematodes cause root swellings or root galls, resulting in yellowing and premature abscission of the leaves. Since nematicide treatments are expensive, it is important to use clean land, not replanting papaya in the same field.
The oriental fruit fly (Dacus dorsalis) is a major concern of papaya- importing countries such as Japan and the United States. The flies deposit their eggs in ripe fruit. Fruit should be harvested at the mature green stage. Over-ripe and infested fruit should be buried. Male flies can be baited by placing a cotton ball dipped in methyl eugenol-malathion solution inside trap bottles positioned every 25 m throughout the plantation.
Mites (Tetranychus kansawai and Brevipalpus californicus) suck the plant sap, leading to poor plant growth and blemishes on the fruit. Predatory mites generally provide adequate control, an additional reason for restraint in the use of acaricides or insecticides with miticidal action. Aphid (Aphis gossypii, Myzus persicae) infestation weakens the plants and aphids also transmit virus diseases. Removing alternative hosts and the presence of natural predators can effectively reduce aphid populations. Spraying insecticide on the undersides of the leaves is also an effective control measure.
Harvesting
The appearance of traces of yellow colour on the fruit indicates that it is ready for harvesting. The fruit is twisted until the stalk snaps off or cut with a sharp knife. A long pole or a ladder is needed for tall plants.
For papain production, latex is collected by tapping the green unripe fruit. Four longitudinal incisions, skin-deep and 2—3 cm apart, are made with a sharp, non-corrosive rod (glass, plastic or horn). Latex is collected in a clean glass or porcelain container and dried. Fruits may be tapped once a week, until they show signs of ripening. The operation is best done early in the morning (before 10 a.m.). Dried latex is processed in the laboratory. Tapping results in ugly scars on the fruit, although quality is unaffected. Tapped fruit can be processed or used as animal feed.
For papain production, latex is collected by tapping the green unripe fruit. Four longitudinal incisions, skin-deep and 2—3 cm apart, are made with a sharp, non-corrosive rod (glass, plastic or horn). Latex is collected in a clean glass or porcelain container and dried. Fruits may be tapped once a week, until they show signs of ripening. The operation is best done early in the morning (before 10 a.m.). Dried latex is processed in the laboratory. Tapping results in ugly scars on the fruit, although quality is unaffected. Tapped fruit can be processed or used as animal feed.
Yield
In the Philippines where papaya is mainly grown in home gardens or as intercrop, the national average yield is only 15 t/ha per year. Yield in ringspot-infested areas is far below this figure, but in well-managed commercial papaya farms in the southern Philippines where the disease is not yet present, the yield is over 30 t/ha. 'Subang 6' and 'Taiping 3' average 34 t/ha in Malaysia. Average yield of 'Cariflora' in Florida is 35 t/ha, and more than 40 t/ha is common in Hawaii.
A yield of 200 kg/ha of dried papain is considered good for the first year of tapping; during the second year roughly half as much is collected.
A yield of 200 kg/ha of dried papain is considered good for the first year of tapping; during the second year roughly half as much is collected.
Handling After Harvest
Fruit is placed in wooden or plastic crates and bamboo baskets lined with shredded newspaper or dried banana leaves and transported to the market. In East Java fruit is stacked loose on a truck — each fruit wrapped in a piece of newspaper — and sent to Surabaya and Jakarta; this way of handling entails heavy losses. If intended for export, fruits are graded, wrapped in non-glazed tissue paper and packed in cartons lined with shredded newspaper. Japan and other importing countries with very strict quarantine regulations require pre-shipment treatment as a safeguard against fruit fly infestation.
Genetic Resources
Modest collections of papaya are maintained by the Malaysian Research and Development Institute (MARDI) and the Institute of Plant Breeding, College of Agriculture, University of the Philippines at Los Baños. Research centres in Central and South America (Costa Rica, Mexico, Brazil, Columbia, Peru, Venezuela, etc.), Hawaii, India and Australia are very good sources of germplasm material.
Breeding
Good fruit quality and resistance to diseases are the major objectives in papaya breeding. In addition, short stature, precocity, long peduncles to avoid fruit overcrowding and elimination of female-sterile hermaphroditism and carpellody of the stamens are also being considered. Resistance to ringspot virus has not been found in Carica papaya but is said to occur in other Carica species, including Carica cauliflora Jacq., Carica pubescens Lenné & K. Koch, and Carica pentagona Heilborn. Transfer of ringspot virus resistance from wild Carica species to the papaya should have priority. Although tolerance has been incorporated in some newer cultivars like 'Cariflora' and 'Tainung No. 5', the disease is still limiting the productive life of orchards and is a very serious threat. Interspecific hybridization has not yet yielded results. Researchers have been successful in rescuing hybrid embryos from crosses involving Carica papaya x Carica cauliflora and similar crosses, but there is still the problem of fertility of the F1. Induced variation can supplement this effort. Production of homozygotic diploids via anther culture will hasten the varietal improvement work. Developing stable, true-breeding hermaphrodites will reduce the traditional number of seedlings to be established per hill. If the lethal factor involved kills the embryo due to early endosperm degeneration, then embryo rescue is a promising approach.
Prospects
Papaya is as productive and easy to grow as banana and pineapple. Indeed, in home gardens and local markets it takes an intermediate position between banana and pineapple, but in the larger markets and in world trade papaya lags far behind. The main reasons must be the perishable nature of the fruit and, in comparison with pineapple, the limited appeal of the processed products.
The expanding world trade is based on the small fruits of cultivars in the Solo group which lend themselves much better to packing and shipping than the traditional large fruits. The small-fruited cultivars have also gained a foothold in South-East Asia, but the high cost of packing and transport precludes a rapid increase in exports. Unless new developments favour processing, papaya will continue to be mainly a fruit for home gardeners and small fruit growers.
It is not clear what happened to papain production after Tanzania was superseded by South America as the leading producer in the 1960s; hence little can be said about the scope for papain production in South-East Asia.
The expanding world trade is based on the small fruits of cultivars in the Solo group which lend themselves much better to packing and shipping than the traditional large fruits. The small-fruited cultivars have also gained a foothold in South-East Asia, but the high cost of packing and transport precludes a rapid increase in exports. Unless new developments favour processing, papaya will continue to be mainly a fruit for home gardeners and small fruit growers.
It is not clear what happened to papain production after Tanzania was superseded by South America as the leading producer in the 1960s; hence little can be said about the scope for papain production in South-East Asia.
Literature
Abdon, A.C., 1980. Food composition tables recommended for use in the Philippines. 5th revised edition. Food and Nutrition Research Institute, Manila. 313 pp.
Chan, Y.K., 1975. Papaya cultivation. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute, Serdang. 6 pp.
Chan, H.T. & Tang, C.S., 1978. The chemistry and biochemistry of papaya. In: Inglett, G.E. & Charolambous, G. (Editors): Tropical Foods, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York. pp. 33—55.
Conover, R.A., Litz, R.E. & Malo, S.E., 1986. 'Cariflora', a papaya ringspot virus tolerant papaya for South Florida and the Caribbean. HortScience 21: 1072.
Horovitz, S. & Jimenez, H., 1978. Cruzamientos interspecificos e intergenéricos en Caricaceas y sus implicaciones fitotécnicas. [Interspecific and intergeneric crosses in Caricaceae and their agronomical implications]. Agronomía Tropical (Maracay) 17: 323—343.
Manshardt, R.M. & Wenslaff, T.F., 1989. Interspecific hybridization of papaya with other Carica species. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 114: 689—694.
PCARRD, 1984. The Philippines recommends for papaya. Los Baños, Laguna. 58 pp.
Storey, W.B., 1969. Papaya (Carica papaya L.). In: Ferwerda, F.P. & Wit, F. (Editors): Outlines of perennial crop breeding in the tropics. H. Veenman en Zonen BV, Wageningen. pp. 389—407.
Chan, Y.K., 1975. Papaya cultivation. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute, Serdang. 6 pp.
Chan, H.T. & Tang, C.S., 1978. The chemistry and biochemistry of papaya. In: Inglett, G.E. & Charolambous, G. (Editors): Tropical Foods, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York. pp. 33—55.
Conover, R.A., Litz, R.E. & Malo, S.E., 1986. 'Cariflora', a papaya ringspot virus tolerant papaya for South Florida and the Caribbean. HortScience 21: 1072.
Horovitz, S. & Jimenez, H., 1978. Cruzamientos interspecificos e intergenéricos en Caricaceas y sus implicaciones fitotécnicas. [Interspecific and intergeneric crosses in Caricaceae and their agronomical implications]. Agronomía Tropical (Maracay) 17: 323—343.
Manshardt, R.M. & Wenslaff, T.F., 1989. Interspecific hybridization of papaya with other Carica species. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 114: 689—694.
PCARRD, 1984. The Philippines recommends for papaya. Los Baños, Laguna. 58 pp.
Storey, W.B., 1969. Papaya (Carica papaya L.). In: Ferwerda, F.P. & Wit, F. (Editors): Outlines of perennial crop breeding in the tropics. H. Veenman en Zonen BV, Wageningen. pp. 389—407.
Author(s)
V.N. Villegas
Correct Citation of this Article
Villegas, V.N., 1991. Carica papaya L.. In: Verheij, E.W.M. and Coronel, R.E. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 2: Edible fruits and nuts. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.