Record Number
2434
PROSEA Handbook Number
12(3): Medicinal and poisonous plants 3
Taxon
Bauhinia purpurea L.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Bauhinia in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Bauhinia in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
Protologue
Sp. pl. 1: 375 (1753).
Synonyms
Bauhinia triandra Roxb. (1832), Bauhinia castrata Blanco (1837), Phanera purpurea (L.) Benth. (1852).
Vernacular Names
Orchid tree, purple bauhinia (En). Indonesia: aroy kupu-kupu (Sundanese), suwoto (Javanese). Malaysia: tapak kuda (Peninsular), lupit (Sabah). Philippines: alibangbang (Tagalog). Thailand: sieo dok daeng, sieo waan (northern). Vietnam: m[os]ng b[of] t[is]m.
Distribution
Native to tropical Asia, cultivated throughout the tropics, including South-East Asia; it occurs occasionally as an escape from cultivation.
Uses
In Peninsular Malaysia and Thailand the leaves are used for poulticing sores and boils. In India, the bark is extensively applied in glandular diseases and as a poison antidote. It is well known for its astringent, anthelmintic, carminative and diuretic effects and is used in diarrhoea. The leaves are administered as a cough medicine. The flowers are said to be laxative and used in curries and pickles.
Observations
A shrub or small tree up to 10 m tall, young branches glabrescent; leaves suborbicular, up to 12 cm x 12 cm, bifid up to 1/3—1/2, base rounded to cordate, apex of lobes rounded to acute, 9—13-veined, stipules minute, 1—2 mm long; inflorescence a 6—10-flowered raceme; flower buds club-shaped, velvety, 3—4 cm long, hypanthium turbinate, calyx splitting spathaceous, petals narrowly lanceolate, 3—5 cm long, claws 0.5—1 cm long, pink to dark purple; fertile stamens 3, staminodes 5—6; fruit strap-shaped, not septate, 20—25 cm x 1.5—2.5 cm, c. 10-seeded, glabrous, dehiscent; seeds orbicular, up to 15 mm in diameter.
Image
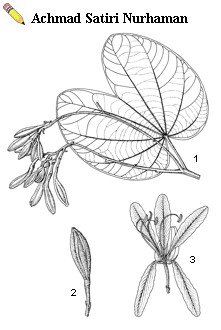 | Bauhinia purpurea L. - 1, twig with flower buds; 2, flower bud; 3, flower |
Selected Sources
[121]Burkill, I.H., 1966. A dictionary of the economic products of the Malay Peninsula. Revised reprint. 2 volumes. Ministry of Agriculture and Co- operatives, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Vol. 1 (A—H) pp. 1—1240, Vol. 2 (I— Z) pp. 1241—2444.
[178]Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 774 pp.
[206]de Wit, H.C.D., 1956. A revision of Malaysian Bauhinieae. Reinwardtia 3: 381—539.
[247]Flora Malesiana (various editors), 1950—. Foundation Flora Malesiana. Rijksherbarium/Hortus Botanicus, Leiden, the Netherlands.
[654]Mukherjee, P.K. et al., 1998. Studies on the anti-diarrhoeal profiles of Bauhinia purpurea Linn leaves (Fam. Caesalpiniaceae) extract. Natural Product Sciences 4(4): 234—237.
[719]Panda, S. & Kar, A., 1999. Withania somnifera and Bauhinia purpurea in the regulation of circulating thyroid hormone concentrations in female mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 67(2): 233—239.
[731]Perry, L.M., 1980. Medicinal plants of East and Southeast Asia. Attributed properties and uses. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States & London, United Kingdom. 620 pp.
[965]Verdcourt, B., 1979. A manual of New Guinea legumes. Botany Bulletin No 11. Office of Forests, Division of Botany, Lae, Papua New Guinea. 645 pp.
[178]Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 774 pp.
[206]de Wit, H.C.D., 1956. A revision of Malaysian Bauhinieae. Reinwardtia 3: 381—539.
[247]Flora Malesiana (various editors), 1950—. Foundation Flora Malesiana. Rijksherbarium/Hortus Botanicus, Leiden, the Netherlands.
[654]Mukherjee, P.K. et al., 1998. Studies on the anti-diarrhoeal profiles of Bauhinia purpurea Linn leaves (Fam. Caesalpiniaceae) extract. Natural Product Sciences 4(4): 234—237.
[719]Panda, S. & Kar, A., 1999. Withania somnifera and Bauhinia purpurea in the regulation of circulating thyroid hormone concentrations in female mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 67(2): 233—239.
[731]Perry, L.M., 1980. Medicinal plants of East and Southeast Asia. Attributed properties and uses. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States & London, United Kingdom. 620 pp.
[965]Verdcourt, B., 1979. A manual of New Guinea legumes. Botany Bulletin No 11. Office of Forests, Division of Botany, Lae, Papua New Guinea. 645 pp.
Author(s)
J.W.A. Ridder-Numan
Correct Citation of this Article
Ridder-Numan, J.W.A., 2003. Bauhinia purpurea L.. In: Lemmens, R.H.M.J. and Bunyapraphatsara, N. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 12(3): Medicinal and poisonous plants 3. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.