Record Number
269
PROSEA Handbook Number
12(1): Medicinal and poisonous plants 1
Taxon
Ficus benghalensis L.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Ficus in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Ficus in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
Protologue
Sp. pl. 2: 1059 (1753).
Synonyms
Ficus indica L. (1753), Ficus lasiophylla Link (1822), Ficus banyana Oken (1841).
Vernacular Names
Banyan tree, Indian banyan (En). Indonesia: beringin India. Malaysia: banyan (general), ara tandok, bohdi (Peninsular). Burma (Myanmar): pyi-nyaung. Thailand: krang, ni khrot (central). Vietnam: da l[as] tr[of]n.
Distribution
Originally from India and Pakistan but widely planted in Indo-China, Thailand and in the Malesian region and locally naturalized.
Uses
The leaves are used to remedy dysentery and diarrhoea, and are applied to abscesses as a poultice to promote suppurations and discharge of pus. In a decoction with toasted rice, the leaves are used as a diaphoretic. The bark is tonic and diuretic, an infusion is antidiabetic and a decoction is used as an astringent in leucorrhoea. A decoction of root fibres is useful against gonorrhoea, whereas the tender ends of aerial roots are used for obstinate vomiting. An infusion of the twigs is good for haemoptysis. The milky latex is used against pains and fever, rheumatism and lumbago, toothache, and applied to cracked and inflamed soles. The concentrated latex plus fruit is aphrodisiac and used to treat spermatorrhoea and gonorrhoea. The fruit is tonic and has a cooling effect.
Observations
A deciduous to evergreen, wide-spreading banyan up to 20(-25) m tall, with copious aerial roots, bark surface smooth, grey; leaves arranged spirally, ovate or broadly ovate to elliptical, 10-30 cm x 7-20 cm, base cordate, apex blunt to rounded, margin entire, with 5-7 pairs of lateral veins, puberulous below, stipules 1.5-2.5 cm long; figs paired, sessile, globose to depressed globose, 15-25 mm in diameter, puberulous, orange to red or pinkish-red when ripe; male flowers many, shortly stipitate, with 2-3 tepals and 1 stamen, female flowers sessile, with 3-4 tepals. Ficus benghalensis occurs in evergreen to deciduous lowland forest.
Image
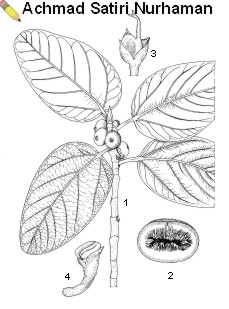 | Ficus benghalensis L. — 1, fruiting twig; 2, halved fig; 3, female flower; 4, male flower |
Selected Sources
[9] Achrekar, S., Kaklij, G.S., Pote, M.S. & Kelkar, S.M., 1991. Hypoglycemic activity of Eugenia jambolana and Ficus bengalensis: mechanism of action. In-Vivo 5(2): 143-147.
[167] Boer, E. & Sosef, M.S.M., 1998. Ficus L. In: Sosef, M.S.M., Hong, L.T. & Prawirohatmodjo, S. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 5(3). Timber trees: Lesser-known timbers. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, the Netherlands. pp. 232-23
[248] Chew, W.-L., 1989. Moraceae. In: George, A.S. (Editor): Flora of Australia. Vol. 3. Hamamelidales to Casuarinales. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, Australia. pp. 15-68.
[281] Corner, E.J.H., 1965. Check-list of Ficus in Asia and Australia. Gardens' Bulletin, Singapore 21: 1-186.
[284] Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 774 pp.
[478] Ghafoor, A., 1985. Moraceae. In: Nasir, E. & Ali, S.I. (Editors): Flora of Pakistan No 171. National Herbarium (Stewart Collection), Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, Islamabad, Pakistan. 54 pp.
[795] Kumar, R.V. & Augusti, K.T., 1989. Antidiabetic effect of a leucocyanidin derivative isolated from the bark of Ficus bengalensis L. Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics 26: 400-404.
[874] Locher, C.P., Witrouw, M., De Bethune, M.P., Burch, M.T., Mover, H.F., Davis, H., Lasure, A., Pauwels, R., De Clerq, E. & Elietinck, A.J., 1996. Antiviral activity of Hawaiian medicinal plants against human immuno deficiency Type 1 (HIV-1). Phytomedicine 2(3): 259-264.
[921] Matthew, K.M., 1981-1988. The flora of the Tamilnadu Carnatic. 4 volumes. The Rapinat Herbarium, St. Joseph's College, Tiruchirapalli, India.
[1115] Patel, G.N., 1986. Ayurveda: The traditional medicine in India. In: Steiner, R.P. (Editor): Folk medicine, the art and science. American Chemical Society, Washington D.C., United States.
[1178] Quisumbing, E., 1978. Medicinal plants of the Philippines. Katha Publishing Co., Quezon City, the Philippines. 1262 pp.
[1191] Rai, S.N., Nagaveni, H.C. & Ananth Padmanabha, H.S., 1988. Germination and nursery technique of four species of Ficus. Indian Forester 114(2): 63-68.
[1289] Sastrapradja, S. & Afristiani, J.J., 1984. Kerabat beringin [The genus Ficus]. Seri Sumber Daya Alam 115. Lembaga Biologi Nasional - LIPI, Bogor, Indonesia. 118 pp.
[1404] Subramanian, P.M. & Misra, G.S., 1978. Chemical constituents of Ficus bengalensis. Polish Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacy 30: 559-562.
[167] Boer, E. & Sosef, M.S.M., 1998. Ficus L. In: Sosef, M.S.M., Hong, L.T. & Prawirohatmodjo, S. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 5(3). Timber trees: Lesser-known timbers. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, the Netherlands. pp. 232-23
[248] Chew, W.-L., 1989. Moraceae. In: George, A.S. (Editor): Flora of Australia. Vol. 3. Hamamelidales to Casuarinales. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, Australia. pp. 15-68.
[281] Corner, E.J.H., 1965. Check-list of Ficus in Asia and Australia. Gardens' Bulletin, Singapore 21: 1-186.
[284] Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd Edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. 774 pp.
[478] Ghafoor, A., 1985. Moraceae. In: Nasir, E. & Ali, S.I. (Editors): Flora of Pakistan No 171. National Herbarium (Stewart Collection), Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, Islamabad, Pakistan. 54 pp.
[795] Kumar, R.V. & Augusti, K.T., 1989. Antidiabetic effect of a leucocyanidin derivative isolated from the bark of Ficus bengalensis L. Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics 26: 400-404.
[874] Locher, C.P., Witrouw, M., De Bethune, M.P., Burch, M.T., Mover, H.F., Davis, H., Lasure, A., Pauwels, R., De Clerq, E. & Elietinck, A.J., 1996. Antiviral activity of Hawaiian medicinal plants against human immuno deficiency Type 1 (HIV-1). Phytomedicine 2(3): 259-264.
[921] Matthew, K.M., 1981-1988. The flora of the Tamilnadu Carnatic. 4 volumes. The Rapinat Herbarium, St. Joseph's College, Tiruchirapalli, India.
[1115] Patel, G.N., 1986. Ayurveda: The traditional medicine in India. In: Steiner, R.P. (Editor): Folk medicine, the art and science. American Chemical Society, Washington D.C., United States.
[1178] Quisumbing, E., 1978. Medicinal plants of the Philippines. Katha Publishing Co., Quezon City, the Philippines. 1262 pp.
[1191] Rai, S.N., Nagaveni, H.C. & Ananth Padmanabha, H.S., 1988. Germination and nursery technique of four species of Ficus. Indian Forester 114(2): 63-68.
[1289] Sastrapradja, S. & Afristiani, J.J., 1984. Kerabat beringin [The genus Ficus]. Seri Sumber Daya Alam 115. Lembaga Biologi Nasional - LIPI, Bogor, Indonesia. 118 pp.
[1404] Subramanian, P.M. & Misra, G.S., 1978. Chemical constituents of Ficus bengalensis. Polish Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacy 30: 559-562.
Author(s)
J.P. Rojo, F.C. Pitargue & M.S.M. Sosef
Correct Citation of this Article
Rojo, J.P., Pitargue, F.C. & Sosef, M.S.M., 1999. Ficus benghalensis L.. In: de Padua, L.S., Bunyapraphatsara, N. and Lemmens, R.H.M.J. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 12(1): Medicinal and poisonous plants 1. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.