Record Number
413
PROSEA Handbook Number
12(1): Medicinal and poisonous plants 1
Taxon
Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Schefflera in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
This article should be read together with the article on the genus: Schefflera in the Handbook volume indicated above in this database.
Protologue
Bot. Journ. Linn. Soc. 140: 314 (1990).
Synonyms
Vitis heptaphylla L. (1771), Schefflera octophylla (Lour.) Harms (1894).
Vernacular Names
Laos: ko tan. Vietnam: ch[aa]n chim, nam s[aa]m.
Distribution
Burma (Myanmar), Thailand, Indo-China, the Philippines (Batan Island), southern China, Taiwan, the Ryukyu Islands and southernmost Japan.
Uses
The bark is widely used in folk medicine for its diuretic properties and as a tonic. The ashes are sometimes used to treat dropsy. In Hong Kong the fresh branchlets are used as a wash to soothe itching of the skin.
Observations
A small to medium-sized, semi-deciduous or evergreen tree up to 25 m tall, bole up to 80 cm in diameter; leaves palmately 6-8(-11)-foliolate, polymorphic, petiole 8-35 cm long, leaflets elliptical to ovate-elliptical, 7-20 cm x 3-6 cm, base attenuate, apex narrowly pointed, margin entire, glabrous, petiolules unequal, 1-5 cm long; inflorescence a well-developed panicle with hairy branches; flowers in many-flowered umbellules or sometimes solitary at the top of secondary axes; flowers 5-merous, ovary 5-8(-10)-locular; fruit globular, 3-4 mm in diameter, black. Schefflera heptaphylla is found in relatively open forest and forest edges. In southernmost Japan it occurs near sea-level; in the Ryukyu Islands up to 600 m elevation. Southward in the tropics its maximum altitude rises to 1200(-1400) m, or it even becomes entirely montane. Its distribution corresponds with the 20°C average January isotherm. Exploited from wild sources as well as from cultivation, this species can probably be grown easily at higher elevations in the Malesian region.
Image
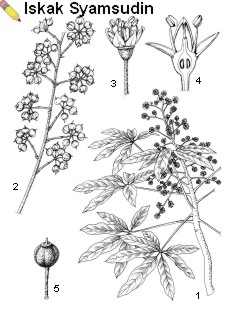 | Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin — 1, flowering twig; 2, part of infructescence; 3, flower; 4, flower in longitudinal section; 5, fruit |
Selected Sources
[363] Doan Thi Nhu, Nguyen Thuong Thuc, Do Huy Bich & Vu Thuy Huyen (Editors), 1991. Les plants médicinales au Vietnam. Livre 1. Médicine traditionelle et pharmacopée [The medicinal plants of Vietnam. Volume 1. Traditional medicine and pharmacopoeia]. Agence de coopération Culturelle et Technique, Paris, France. 201 pp.
[435] Frodin, D.G., 1990. Studies in Schefflera (Araliaceae), IV. The identity of Vitis heptaphylla L., a long-misplaced Linnean ivy tree. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 104: 309-424.
[884] Maeda, C., Ohtani, K., Kasai, R., Yamasaki, K., Nguyen, M.D., Nguyen, T.N. & Nguyen, K.Q., 1994. Oleanane and ursane glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 37(4): 1131-1137.
[1035] Nguyen Van Duong, 1993. Medicinal plants of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos. Mekong Printing, Santa Ana, California, United States. 528 pp.
[1070] Ohashi, H., 1993. Araliaceae. In: Huang, T.-C. (Editor): Flora of Taiwan. 2nd Edition. Vol. 3. Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan, Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China. pp. 986-1009.
[1126] Perry, L.M., 1980. Medicinal plants of East and Southeast Asia. Attributed properties and uses. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States & London, United Kingdom. 620 pp.
[1128] Pételot, A., 1952-1954. Les plantes médicinales du Cambodge, du Laos et du Vietnam [The medicinal plants of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam]. 4 volumes. Centre National de Recherches Scientifiques et Techniques, Saigon, Vietnam.
[1314] Shang, C.B., 1984. Le genre Schefflera (Araliacées) en Chine et en Indochine. Candollea 39: 453-486.
[1416] Sung, T.V. & Adam, G., 1991. A sulphated triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(8): 2717-2720.
[1417] Sung, T.V., Lavaud, C., Porzel, A., Steglich, W. & Adam, G., 1992. Triterpenoids and their glycosides from the bark of Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 31(1): 227-231.
[1418] Sung, T.V., Peter-Katalinic, J. & Adam, G., 1991. A bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(11): 3717-3720.
[1419] Sung, T.V., Steglich, W. & Adam, G., 1991. Triterpene glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(7): 2349-2356.
[1526] Viguier, R., 1923. Araliacées [Araliaceae]. In: Gagnepain, F. (Editor): Flore générale de l'Indo-Chine [General flora of Indo-China]. Vol. 2. Masson & Cie, Paris, France. pp. 1158-1182.
[435] Frodin, D.G., 1990. Studies in Schefflera (Araliaceae), IV. The identity of Vitis heptaphylla L., a long-misplaced Linnean ivy tree. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 104: 309-424.
[884] Maeda, C., Ohtani, K., Kasai, R., Yamasaki, K., Nguyen, M.D., Nguyen, T.N. & Nguyen, K.Q., 1994. Oleanane and ursane glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 37(4): 1131-1137.
[1035] Nguyen Van Duong, 1993. Medicinal plants of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos. Mekong Printing, Santa Ana, California, United States. 528 pp.
[1070] Ohashi, H., 1993. Araliaceae. In: Huang, T.-C. (Editor): Flora of Taiwan. 2nd Edition. Vol. 3. Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan, Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China. pp. 986-1009.
[1126] Perry, L.M., 1980. Medicinal plants of East and Southeast Asia. Attributed properties and uses. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States & London, United Kingdom. 620 pp.
[1128] Pételot, A., 1952-1954. Les plantes médicinales du Cambodge, du Laos et du Vietnam [The medicinal plants of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam]. 4 volumes. Centre National de Recherches Scientifiques et Techniques, Saigon, Vietnam.
[1314] Shang, C.B., 1984. Le genre Schefflera (Araliacées) en Chine et en Indochine. Candollea 39: 453-486.
[1416] Sung, T.V. & Adam, G., 1991. A sulphated triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(8): 2717-2720.
[1417] Sung, T.V., Lavaud, C., Porzel, A., Steglich, W. & Adam, G., 1992. Triterpenoids and their glycosides from the bark of Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 31(1): 227-231.
[1418] Sung, T.V., Peter-Katalinic, J. & Adam, G., 1991. A bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(11): 3717-3720.
[1419] Sung, T.V., Steglich, W. & Adam, G., 1991. Triterpene glycosides from Schefflera octophylla. Phytochemistry 30(7): 2349-2356.
[1526] Viguier, R., 1923. Araliacées [Araliaceae]. In: Gagnepain, F. (Editor): Flore générale de l'Indo-Chine [General flora of Indo-China]. Vol. 2. Masson & Cie, Paris, France. pp. 1158-1182.
Author(s)
Nguyen Tap & M.S.M. Sosef
Correct Citation of this Article
Nguyen Tap & Sosef, M.S.M., 1999. Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. In: de Padua, L.S., Bunyapraphatsara, N. and Lemmens, R.H.M.J. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 12(1): Medicinal and poisonous plants 1. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.