Record Number
4816
PROSEA Handbook Number
5(3): Timber trees; Lesser-known timbers
Taxon
Albizia Durazz.
Protologue
Mag. Tosc. 3: 11 (1772).
Family
LEGUMINOSAE
Chromosome Numbers
x = 13; A. chinensis, A. lebbeck, A. lebbekoides, A. procera: 2n = 26
Vernacular Names
Albizia (En). Malaysia: batai, batai batu, kungkur (general).
Origin and Geographic Distribution
Albizia comprises about 150 species and has a pantropical distribution, with centres of speciation in Africa, Madagascar and tropical America. It occurs throughout the Asian tropics and 20 species are indigenous within the Malesian region. A. lebbeck is planted and naturalized throughout the tropics.
Uses
In South-East Asia the wood of Albizia is quite variable in quality and is used for house construction (posts, beams), bridge construction, mine timber, boat building, dugout canoes, spokes and wheel rims, furniture and cabinet work, framework, mouldings, shuttering, interior finish, parquet and strip flooring, panelling, partitioning, oars, casks, oil presses, agricultural implements, carving, musical instruments, picture frames, turnery, gunstocks, novelties, fancy boxes, matches and matchboxes. The wood is suitable for the production of veneer and plywood, sometimes even for decorative veneers, and produces good firewood and charcoal. In the Philippines A. acle is regarded a suitable substitute for black walnut (Juglans nigra L.) from the temperate zones.
Albizia is frequently planted as a shade tree for various crops like tea and coffee and to improve the soil fertility, occasionally as an ornamental in parks and along roads. A. chinensis, A. lebbeck and A. procera are also planted to rehabilitate degraded sites and in fire- and wind-breaks. The trunk of A. lebbeck and A. procera yields a gum which is similar to arabic gum. A red dye and tannin used to be extracted from the bark, especially that of A. lebbekoides. The bark of the latter is used in Cambodia as a remedy for colic, and in the Philippines it is put into fermenting sugar cane juice to make an intoxicating liquor. The bark, which contains saponin, has been used as a substitute for soap (especially A. saponaria), as a fish poison, and shows insecticidal activity. Leaves of some species are sometimes used as fodder for cattle. The outer bark of A. splendens is used for lighting fires in humid conditions.
Albizia is frequently planted as a shade tree for various crops like tea and coffee and to improve the soil fertility, occasionally as an ornamental in parks and along roads. A. chinensis, A. lebbeck and A. procera are also planted to rehabilitate degraded sites and in fire- and wind-breaks. The trunk of A. lebbeck and A. procera yields a gum which is similar to arabic gum. A red dye and tannin used to be extracted from the bark, especially that of A. lebbekoides. The bark of the latter is used in Cambodia as a remedy for colic, and in the Philippines it is put into fermenting sugar cane juice to make an intoxicating liquor. The bark, which contains saponin, has been used as a substitute for soap (especially A. saponaria), as a fish poison, and shows insecticidal activity. Leaves of some species are sometimes used as fodder for cattle. The outer bark of A. splendens is used for lighting fires in humid conditions.
Production and International Trade
In Sabah the lightweight wood of A. chinensis and A. pedicellata is traded as "batai"" together with the wood of Paraserianthes falcataria (L.) I.C. Nielsen, the medium-weight timber as "batai batu"". In 1992 "kungkur"" timber (A. splendens) was exported from Sabah together with "petai"" (Parkia spp.), as a total volume of 2100 m3 of sawn timber and a total value of about US$ 480 000. In 1996 Papua New Guinea exported about 11 810 m3 of "brown albizia"" (A. procera) logs at an average free-on-board (FOB) price of US$ 99/m3.
Properties
Albizia yields a lightweight to medium-weight, occasionally heavy hardwood with a density of 315-950 kg/m3 at 15% moisture content. Important species and their density at 15% moisture content are: A. pedicellata 315-450 kg/m3, A. chinensis 320-640 kg/m3, A. splendens 470-845 kg/m3, A. lebbekoides 500-900 kg/m3 and A. procera 600-950 kg/m3. Heartwood pale brown to dark reddish-brown or golden-brown with paler streaks and bands, often similar to Juglans spp., sharply demarcated from the white to straw-coloured sometimes very wide sapwood; grain sometimes straight but usually interlocked or wavy; texture moderately fine to moderately coarse and even. Maximum sapwood width of 12-15-year-old trees is 10-12 cm. Growth rings sometimes distinct due to contrast in density of the fibres between earlywood and latewood; vessels medium-sized to very large, solitary and in radial multiples of 2-3(-4) with a tendency to oblique arrangement, vessels with white, yellow or dark gum-like or solid deposits; parenchyma moderately abundant, apotracheal diffuse and paratracheal vasicentric and aliform, sometimes confluent, also apotracheal in marginal bands; rays very fine to moderately fine; ripple marks absent; pith flecks occasionally present.
Shrinkage is low to moderate or high, but the wood seasons well with little or no degrade, although logs of some species are liable to develop heart shakes unless converted green. Boards of A. splendens 13 mm and 38 mm thick take respectively 3.5 and 4.5 months to air dry. Kiln drying gives good results. The wood is soft and fairly weak (lightweight species), or moderately hard and strong (medium-weight species); that of A. procera is reported hard, strong and tough. The wood is somewhat difficult to work with hand and machine tools and tends to pick up in planing and moulding; the cutting angle should not exceed 20°. The wood of A. splendens, however, has good working properties and finishes well, both in the green as well as in the air-dry state. It polishes excellently. The wood is non-durable to durable when in contact with the ground or exposed to the weather. In a graveyard test in the Philippines the average service life was 10 years for A. acle and A. procera, 3 years for A. saponaria and only 16 months for A. chinensis. The wood is resistant to dry-wood termites but the sapwood is susceptible to Lyctus. The heartwood is extremely resistant to impregnation, the sapwood is permeable. The energy value of the wood is 19 500-21 500 kJ/kg.
Sawdust may cause irritation to mucous membranes. The bark of older trees of A. lebbekoides contains 15-20% tannin.
See also the tables on microscopic wood anatomy and wood properties.
Shrinkage is low to moderate or high, but the wood seasons well with little or no degrade, although logs of some species are liable to develop heart shakes unless converted green. Boards of A. splendens 13 mm and 38 mm thick take respectively 3.5 and 4.5 months to air dry. Kiln drying gives good results. The wood is soft and fairly weak (lightweight species), or moderately hard and strong (medium-weight species); that of A. procera is reported hard, strong and tough. The wood is somewhat difficult to work with hand and machine tools and tends to pick up in planing and moulding; the cutting angle should not exceed 20°. The wood of A. splendens, however, has good working properties and finishes well, both in the green as well as in the air-dry state. It polishes excellently. The wood is non-durable to durable when in contact with the ground or exposed to the weather. In a graveyard test in the Philippines the average service life was 10 years for A. acle and A. procera, 3 years for A. saponaria and only 16 months for A. chinensis. The wood is resistant to dry-wood termites but the sapwood is susceptible to Lyctus. The heartwood is extremely resistant to impregnation, the sapwood is permeable. The energy value of the wood is 19 500-21 500 kJ/kg.
Sawdust may cause irritation to mucous membranes. The bark of older trees of A. lebbekoides contains 15-20% tannin.
See also the tables on microscopic wood anatomy and wood properties.
Botany
Evergreen to briefly deciduous shrubs or small to fairly large trees up to 35(-50) m tall, rarely armed lianas; bole straight or rather crooked, short or branchless for up to 20 m, up to 100(-150) cm in diameter, sometimes with small buttresses; bark surface smooth to closely fissured, lenticellate, grey to blackish, inner bark coarsely fibrous, reddish-brown or yellow to cream; crown usually flattened. Leaves arranged spirally, bipinnate, rachis and pinnae with extrafloral nectaries; leaflets many, opposite, entire; stipules caducous. Flowers in pedunculate glomerules or corymbs which are axillary or aggregated into a terminal or axillary panicle, 5-merous, often dimorphic, the marginal flowers in each head bisexual, the central ones male; calyx and corolla connate, valvate; stamens many, united into a tube below, long exserted; ovary superior, 1-locular with many ovules, style filiform. Fruit a straight, flat, dehiscent to indehiscent pod. Seed circular to ellipsoid, more or less flattened, the hard testa with pleurogram. Seedling with epigeal germination; cotyledons emergent, fleshy; hypocotyl elongated; first 2 leaves opposite or subopposite, subsequent ones arranged spirally, initially pinnate or bipinnate from the start.
A. lebbeck develops according to Troll's architectural tree model, characterized by only plagiotropic axes and built by continuous superposition of branches thus forming a sympodial stem. Albizia species flower shortly after the appearance of new leaves. In Java A. lebbekoides flowers in March-June and fruits in July-November. In Central Java A. procera flowers in April-June with the major fruit production in August and September, in East Java these periods are January-October and May-October, respectively. Pollination is generally by bees or butterflies, but bird pollination has also been recorded. In species with indehiscent pods the dispersal unit is the entire pod. The dispersal agent is water, except for A. pedicellata for which wind dispersal is reported.
Albizia belongs to the subfamily Mimosoideae and the tribe Ingeae, together with e.g. the genera Archidendron and Paraserianthes. The distinction between the various genera is difficult, and has given rise to a complicated nomenclatural history. Albizia is often misspelled as Albizzia, A. lebbekoides often as A. lebbeckioides.
A. lebbeck develops according to Troll's architectural tree model, characterized by only plagiotropic axes and built by continuous superposition of branches thus forming a sympodial stem. Albizia species flower shortly after the appearance of new leaves. In Java A. lebbekoides flowers in March-June and fruits in July-November. In Central Java A. procera flowers in April-June with the major fruit production in August and September, in East Java these periods are January-October and May-October, respectively. Pollination is generally by bees or butterflies, but bird pollination has also been recorded. In species with indehiscent pods the dispersal unit is the entire pod. The dispersal agent is water, except for A. pedicellata for which wind dispersal is reported.
Albizia belongs to the subfamily Mimosoideae and the tribe Ingeae, together with e.g. the genera Archidendron and Paraserianthes. The distinction between the various genera is difficult, and has given rise to a complicated nomenclatural history. Albizia is often misspelled as Albizzia, A. lebbekoides often as A. lebbeckioides.
Image
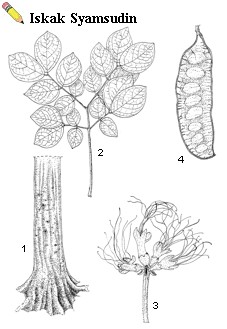 | Albizia saponaria (Lour.) Blume ex Miq. – 1, bole; 2, leaf; 3, inflorescence; 4, pod. |
Ecology
Albizia is usually found scattered or in small groups as a pioneer in open, secondary vegetation or primary deciduous or monsoon forest, savanna and scrub vegetation, from sea-level up to 1700 m altitude; A. chinensis has been cultivated up to 2400 m. They occur in areas with a seasonal climate, often on sandy soils or otherwise well-drained locations. A. dolichadena prefers swamp forest. A. retusa is a littoral species. In the Philippines A. acle is commonly associated with molave (Vitex parviflora A.L. Juss.). In Papua New Guinea A. procera is commonly found in fire-induced grasslands in association with Eucalyptus. Several species can be planted in rocky and shallow sites with a pronounced dry season of at least 4 months.
Silviculture and Management
Albizia is easy to propagate from seed. Direct sowing is often applied, as planting out nursery-grown plants disturbs the long taproot which develops rapidly in young seedlings; in the latter case a survival rate of as low as 4% has been recorded. Some 5-10 seeds per planting hole is usually satisfactory for direct sowing. Cuttings can also be used. Seed should be collected from the tree as it is very susceptible to insect attack and rotting. Seed viability is usually high and seed can be stored for up to 5 years without serious decline in viability. Available seed counts per kg are: A. acle about 240, A. chinensis 49 500-52 000, A. lebbeck 7000-10 500, A. lebbekoides 49 000-59 000 and A. procera 21 000-41 000. Pretreatment of seed with boiling water, concentrated sulphuric acid or by nicking the seed-coat is usually recommended to overcome dormancy, but untreated seed of various species gave 20-80% germination. To assure optimal germination, seeds should be sown in full light. A. lebbeck and A. procera form nitrogen-fixing nodules in the nursery without any inoculation treatment. When sterilized soil was inoculated with Rhizobium obtained from the nodules of a large A. lebbeck tree, however, the seedlings from that tree developed optimally. Seedlings are stumped before planting; in A. lebbeck the stem is cut back to 5 cm, the roots to 15 cm, whereas in A. procera a shoot length of 10-20 cm and a root length of 20-40 cm with a diameter at the collar of 0.5-1.0 cm are recommended. Seedlings up to 1 m tall have been successfully planted as bare-rooted stock. Root cuttings have been successful when taken at least 15 cm long and 1 cm in diameter. In trials in Java the mean annual clear bole volume increment was 7.7-8.5 m3/ha for 15-year-old trees of A. chinensis, 2.8 m3/ha for 12-year-old A. lebbekoides trees and 6.7 m3/ha for 12-year-old A. procera trees. In these trials A. lebbekoides developed a poor stem form due to forking and formation of low and heavy branches. In the Philippines A. chinensis yielded 10-12 m3/ha/year on fertile sites. Lopping the branches for fodder and coppicing are very well tolerated. A rotation of 10-15 years is recommended for A. lebbeck planted for fuelwood, and of 30 years for timber production. The fungus Fusarium oxysporum is a serious disease of several Albizia species, causing gummosis of the vessels and eventually leading to death. In the Philippines the following pests have been observed in A. acle: Lophococcus convexus, a scale insect attacking and killing smaller branches, caterpillars of the faggot worm Clavia cremeri feeding on the leaves, and a flat-headed woodborer, Chrysochroa fulminans, whose larvae feed on the sapwood, possibly girdling the tree inside and whose adults feed on leaves and green bark.
Genetic Resources and Breeding
In the Philippines A. acle is protected and A. procera is considered a vanishing timber tree.
Prospects
As the timber of several Albizia species, especially that of A. acle and A. procera, is of good quality and growth is moderately fast their potential deserves further exploration.
Literature
[12]Aguilar, N.O., Pitargue, F.C. & Cajano, M.O., 1994. Nodulation of legumes in the Philippines. In: Sprent, J.I. & McKey, D. (Editors): Advances in legume systematics 5: The nitrogen factor. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. pp. 25-31.
[47]Ani Bte Sulaiman & Lim, S.C., 1991. Malaysian timbers - kungkur. Timber Trade Leaflet No 114. The Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur & Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 5 pp.
[101]Beekman, H., 1920. 78 Preanger houtsoorten. Beschrijving, afbeelding en determinatietabel [78 Priangan wood species. Description, pictures and identification key]. Mededeelingen No 5. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 186 pp.
[130]Bosbouwproefstation, 1948. Tabellarisch overzicht van de beste kiem-, bewaar- en verzendingswijze van zaad van een aantal boomsoorten en groenbemesters [Tabular summary of the best ways to germinate, store and send seed of some tree and green manure species]. Voorlopig rapport No 38. Bosbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 15 pp.
[162]Burgess, P.F., 1966. Timbers of Sabah. Sabah Forest Records No 6. Forest Department, Sabah, Sandakan. xviii + 501 pp.
[193]Chudnoff, M., 1980. Tropical timbers of the world. Forest Products Laboratory, Forest Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Madison. 831 pp.
[198]Cockburn, P.F., 1976-1980. Trees of Sabah. 2 volumes. Sabah Forest Records No 10. Forest Department Sabah, Sandakan.
[209]Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur. 774 pp.
[218]Dahms, K.-G., 1982. Asiatische, ozeanische und australische Exporthölzer [Asiatic, Pacific and Australian export timbers]. DRW-Verlag, Stuttgart. 304 pp.
[234]de Guzman, E.D., 1975. Conservation of vanishing timber species in the Philippines. In: Williams, J.T., Lamoureux, C.H. & Wulijarni-Soetjipto, N. (Editors): South East Asian plant genetic resources. Proceedings of a Symposium on South East Asian Plant Genetic Resources held at Kopo, Cisarua, 20-22 March 1975. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources, SEAMEO Regional Center for Tropical Biology/BIOTROP, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pertanian and Lembaga Biologi Nasional - LIPI, Bogor. pp. 198-204.
[238]de Vogel, E.F., 1980. Seedlings of dicotyledons. Structure, development, types. Descriptions of 150 woody Malesian taxa. Pudoc, Wageningen. 465 pp.
[259]den Berger, L.G., 1926. Mechanical properties of Dutch East Indian timbers. Korte Mededeelingen No 12. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. viii + 63 pp.
[260]den Berger, L.G., 1926. Houtsoorten der cultuurgebieden van Java en Sumatra's oostkust [Tree species of the cultivated areas of Java and the east coast of Sumatra]. Mededeelingen No 13. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 186 pp.
[261]den Berger, L.G. & Endert, F.H., 1925. Belangrijke houtsoorten van Nederlandsch-Indië, deel I [Important timbers of the Dutch East Indies, part I]. Mededeelingen No 11. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 136 pp.
[267]Desch, H.E., 1941-1954. Manual of Malayan timbers. Malayan Forest Records No 15. 2 volumes. Malaya Publishing House Ltd., Singapore. 762 pp.
[300]Eddowes, P.J., 1977. Commercial timbers of Papua New Guinea, their properties and uses. Forest Products Research Centre, Department of Primary Industry, Port Moresby. xiv + 195 pp.
[304]Eddowes, P.J., 1995-1997. The forests and timbers of Papua New Guinea. (unpublished data).
[308]Eidmann, F.E., 1933. Kiemingsonderzoek bij een 55-tal wildhoutsoorten en groenbemesters [Research on the germination of seeds of some 55 tree species and green manures]. Mededeelingen No 26. Boschbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 156 pp.
[333]Faridah Hanum, I. & van der Maesen, L.J.G. (Editors), 1997. Plant resources of South-East Asia No 11. Auxiliary plants. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden. 389 pp.
[341]Flora Malesiana (various editors), 1950-. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
[343]Flore du Cambodge, du Laos et du Viêtnam (various editors), 1960-. Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris.
[344]Florido, H.B. & Arcilla, R.P., 1994. Akleng-parang. RISE 6(3): 1-5.
[348]Forest Products Research Centre, 1967. Properties and uses of Papua and New Guinea timbers. Forest Products Research Centre, Port Moresby. 30 pp.
[387]Grewal, G.S., 1979. Air-seasoning properties of some Malaysian timbers. Malaysian Forest Service Trade Leaflet No 41. Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur. 26 pp.
[402]Hallé, F., Oldeman, R.A.A. & Tomlinson, P.B., 1978. Tropical trees and forests - an architectural analysis. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York. 441 pp.
[405]Hardjowasono, M.S., 1942. Gewicht en volume van verschillende vrucht- en zaadsoorten [Weight and volume of various fruits and seeds]. Korte Mededelingen No 20. Bosbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 172 pp.
[406]Harker, A.P., Sandels, A. & Burley, J., 1982. Calorific values for wood and bark and a bibliography for fuelwood. Report G 162. Tropical Products Institute, London. 20 pp.
[432]Hensleigh, T.E. & Holaway, B.K., 1988. Agroforestry species for the Philippines. AJA Printers, Malabon. 404 pp.
[436]Heyne, K., 1927. De nuttige planten van Nederlands-Indië [The useful plants of the Dutch East Indies]. 2nd edition, 3 volumes. Departement van Landbouw, Nijverheid en Handel in Nederlandsch-Indië. 1953 pp. (3rd edition, 1950. van Hoeve, 's-Gravenhage/Bandung. 1660 pp.).
[464]Ilic, J., 1990. The CSIRO macro key for hardwood identification. CSIRO, Highett. 125 pp.
[488]Japing, H.W. & Oey Djoen Seng, 1936. Cultuurproeven met wildhoutsoorten in Gadoengan - met overzicht van de literatuur betreffende deze soorten [Trial plantations of non teak wood species in Gadungan (East Java) - with survey of literature about these species]. Korte Mededeelingen No 55, part I to VI. Boschbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 270 pp.
[526]Kartasujana, I. & Martawijaya, A., 1979. Kayu perdagangan Indonesia - sifat dan kegunaannya [Commercial woods of Indonesia - their properties and uses]. Lembaga Penelitian Hasil Hutan, Bogor. 28 pp.
[536]Keating, W.G. & Bolza, E., 1982. Characteristics, properties and uses of timbers. Vol. 1. South-East Asia, northern Australia and the Pacific. Inkata Press Proprietary Ltd., Melbourne, Sydney & London. 362 pp.
[632]Kraemer, J.H., 1951. Trees of the western Pacific region. Tri-State Offset Company, Cincinnatti. 436 pp.
[633]Kramer, F., 1925. Kultuurproeven met industrie-, konstruktie- en luxe-houtsoorten [Investigations regarding the cultivation of different Javanese trees]. Mededeelingen No 12. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 99 pp.
[677]Lee, Y.H. & Chu, Y.P., 1965. The strength properties of Malayan timbers. Malayan Forester 28: 307-319.
[678]Lee, Y.H., Engku Abdul Rahman bin Chik & Chu, Y.P., 1979. The strength properties of some Malaysian timbers. Malaysian Forest Service Trade Leaflet No 34 (revised edition). Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur. 107 pp.
[696]Lemmens, R.H.M.J. & Wulijarni-Soetjipto, N. (Editors), 1991. Plant resources of South-East Asia No 3. Dye and tannin-producing plants. Pudoc, Wageningen. 195 pp.
[697]Letourneux, C., 1957. Tree planting practices in tropical Asia. FAO Forestry Development Paper No 11. FAO, Rome. 172 pp.
[736]Magini, E. & Tulstrup, N.P., 1955. Tree seed notes. I. Arid Areas II. Humid Tropics. FAO Forestry Development Paper 5. FAO, Rome. 354 pp.
[740]Malaysian Timber Industry Board, 1984. Peraturan pemeringkatan kayu keras gergaji Malaysia [The Malaysian grading rules for sawn hardwood timber]. Ministry of Primary Industries, Kuala Lumpur. 109 pp.
[741]Malaysian Timber Industry Board, 1986. 100 Malaysian timbers. Kuala Lumpur. x + 226 pp.
[780]Meniado, J.A. et al., 1975-1981. Wood identification handbook for Philippine timbers. 2 volumes. Government Printing Office, Manila. 370 pp. & 186 pp.
[804]Monsalud, M.R. & Tamolang, F.N., 1969. General information on Philippine hardwoods. Philippine Lumberman 15(7): 14-38.
[816]National Academy of Sciences, 1979. Tropical legumes. Resources for the future. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C. 331 pp.
[829]Ng, F.S.P., 1991-1992. Manual of forest fruits, seeds and seedlings. 2 volumes. Malayan Forest Record No 34. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 997 pp.
[831]Ng, F.S.P. & Mat Asri Ngah Sanah, 1991. Germination and seedling records. Research Pamphlet No 108. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 191 pp.
[839]Nielsen, I., 1985. The Malesian species of Acacia and Albizia (Leguminosae-Mimosoideae). Opera Botanica 81. 50 pp.
[857]Ntumbula, M., Ndiku, L., Tshisand, M. & Ntafu, M., 1990. Induced germination of Albizia lebbeck seeds inoculated with Rhizobium. Nitrogen Fixing Tree Research Reports 8: 116-117.
[861]Oey Djoen Seng, 1951. De soortelijke gewichten van Indonesische houtsoorten en hun betekenis voor de praktijk [Specific gravity of Indonesian woods and its significance for practical use]. Rapport No 46. Bosbouwproefstation, Bogor. 183 pp.
[865]Pader, L.P. & Chicano, D.S., 1993. Langil. RISE 5(1): 6-12.
[899]Pokhriyal, T.C. et al., 1990. Identification of some fast growing leguminous tree species for nitrogen fixation studies. Indian Forester 116: 504-507.
[910]Prinsen, J.H., 1986. Potential of Albizia lebbeck (Mimosaceae) as a tropical fodder tree; a review of literature. Tropical Grasslands 20(2): 78-83.
[933]Research Institute of Wood Industry, 1988. Identification, properties and uses of some Southeast Asian woods. Chinese Academy of Forestry, Wan Shou Shan, Beijing & International Tropical Timber Organization, Yokohama. 201 pp.
[934]Reyes, L.J., 1938. Philippine woods. Technical Bulletin No 7. Commonwealth of the Philippines, Department of Agriculture and Commerce. Bureau of Printing, Manila. 536 pp. + 88 plates.
[955]Rocafort, J.E., Floresca, A.R. & Siopongco, J.O., 1971. Fourth progress report on the specific gravity of Philippine woods. Philippine Architecture, Engineering & Construction Report 18(5): 17-27.
[970]Sadie, V.D. & Cornejo, A.T., 1990. Akle. RISE 2(7): 1-8.
[974]Salvosa, F.M., 1963. Lexicon of Philippine trees. Bulletin No 1. Forest Products Research Institute, College, Laguna. 136 pp.
[1038]Smitinand, T., 1980. Thai plant names. Royal Forest Department, Bangkok. 379 pp.
[1039]Smitinand, T. & Larsen, K. (Editors), 1970-. Flora of Thailand. The Forest Herbarium, Royal Forest Department, Bangkok.
[1086]Tamesis, F. & Aguilar, L., 1951. Important commercial timbers of the Philippines: their properties and uses. Popular Bulletin No 32. Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources. Bureau of Printing, Manila. 83 pp.
[1098]Timber Research and Development Association, 1979. Timbers of the world. Volume 1. Africa, S. America, Southern Asia, S.E. Asia. TRADA/The Construction Press, Lancaster. 463 pp.
[1104]Troup, R.S., 1921. Silviculture of Indian trees. 3 volumes. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
[1163]Verdcourt, B., 1979. A manual of New Guinea legumes. Botany Bulletin No 11. Office of Forests, Division of Botany, Lae. 645 pp.
[1177]von Meyenfeldt, C.F.W.M. et al., 1978. Restoration of devastated inland forests in South Vietnam. Volume III: List of tree species. Agricultural University, Wageningen. 219 pp.
[1198]Weidelt, H.J. (Editor), 1976. Manual of reforestation and erosion control for the Philippines. Schriftenreihe No 22. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Eschborn. 569 pp.
[1199]Werkgoep Tropische Houtteelt, 1973. Bebossing van geërodeerde gronden op Java - bijlage III: Houtsoorten [Afforestation of eroded lands in Java - Annex III: Tree species]. Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen. 128 pp.
[1221]Whitmore, T.C. & Ng, F.S.P. (Editors), 1972-1989. Tree flora of Malaya. A manual for foresters. 4 volumes. Malayan Forest Records No 26. Longman Malaysia Sdn. Berhad, Kuala Lumpur & Petaling Jaya.
[1242]Wong, T.M., 1982. A dictionary of Malaysian timbers. Malayan Forest Records No 30. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 259 pp.
[47]Ani Bte Sulaiman & Lim, S.C., 1991. Malaysian timbers - kungkur. Timber Trade Leaflet No 114. The Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur & Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 5 pp.
[101]Beekman, H., 1920. 78 Preanger houtsoorten. Beschrijving, afbeelding en determinatietabel [78 Priangan wood species. Description, pictures and identification key]. Mededeelingen No 5. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 186 pp.
[130]Bosbouwproefstation, 1948. Tabellarisch overzicht van de beste kiem-, bewaar- en verzendingswijze van zaad van een aantal boomsoorten en groenbemesters [Tabular summary of the best ways to germinate, store and send seed of some tree and green manure species]. Voorlopig rapport No 38. Bosbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 15 pp.
[162]Burgess, P.F., 1966. Timbers of Sabah. Sabah Forest Records No 6. Forest Department, Sabah, Sandakan. xviii + 501 pp.
[193]Chudnoff, M., 1980. Tropical timbers of the world. Forest Products Laboratory, Forest Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Madison. 831 pp.
[198]Cockburn, P.F., 1976-1980. Trees of Sabah. 2 volumes. Sabah Forest Records No 10. Forest Department Sabah, Sandakan.
[209]Corner, E.J.H., 1988. Wayside trees of Malaya. 3rd edition. 2 volumes. The Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur. 774 pp.
[218]Dahms, K.-G., 1982. Asiatische, ozeanische und australische Exporthölzer [Asiatic, Pacific and Australian export timbers]. DRW-Verlag, Stuttgart. 304 pp.
[234]de Guzman, E.D., 1975. Conservation of vanishing timber species in the Philippines. In: Williams, J.T., Lamoureux, C.H. & Wulijarni-Soetjipto, N. (Editors): South East Asian plant genetic resources. Proceedings of a Symposium on South East Asian Plant Genetic Resources held at Kopo, Cisarua, 20-22 March 1975. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources, SEAMEO Regional Center for Tropical Biology/BIOTROP, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pertanian and Lembaga Biologi Nasional - LIPI, Bogor. pp. 198-204.
[238]de Vogel, E.F., 1980. Seedlings of dicotyledons. Structure, development, types. Descriptions of 150 woody Malesian taxa. Pudoc, Wageningen. 465 pp.
[259]den Berger, L.G., 1926. Mechanical properties of Dutch East Indian timbers. Korte Mededeelingen No 12. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. viii + 63 pp.
[260]den Berger, L.G., 1926. Houtsoorten der cultuurgebieden van Java en Sumatra's oostkust [Tree species of the cultivated areas of Java and the east coast of Sumatra]. Mededeelingen No 13. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 186 pp.
[261]den Berger, L.G. & Endert, F.H., 1925. Belangrijke houtsoorten van Nederlandsch-Indië, deel I [Important timbers of the Dutch East Indies, part I]. Mededeelingen No 11. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 136 pp.
[267]Desch, H.E., 1941-1954. Manual of Malayan timbers. Malayan Forest Records No 15. 2 volumes. Malaya Publishing House Ltd., Singapore. 762 pp.
[300]Eddowes, P.J., 1977. Commercial timbers of Papua New Guinea, their properties and uses. Forest Products Research Centre, Department of Primary Industry, Port Moresby. xiv + 195 pp.
[304]Eddowes, P.J., 1995-1997. The forests and timbers of Papua New Guinea. (unpublished data).
[308]Eidmann, F.E., 1933. Kiemingsonderzoek bij een 55-tal wildhoutsoorten en groenbemesters [Research on the germination of seeds of some 55 tree species and green manures]. Mededeelingen No 26. Boschbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 156 pp.
[333]Faridah Hanum, I. & van der Maesen, L.J.G. (Editors), 1997. Plant resources of South-East Asia No 11. Auxiliary plants. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden. 389 pp.
[341]Flora Malesiana (various editors), 1950-. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
[343]Flore du Cambodge, du Laos et du Viêtnam (various editors), 1960-. Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris.
[344]Florido, H.B. & Arcilla, R.P., 1994. Akleng-parang. RISE 6(3): 1-5.
[348]Forest Products Research Centre, 1967. Properties and uses of Papua and New Guinea timbers. Forest Products Research Centre, Port Moresby. 30 pp.
[387]Grewal, G.S., 1979. Air-seasoning properties of some Malaysian timbers. Malaysian Forest Service Trade Leaflet No 41. Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur. 26 pp.
[402]Hallé, F., Oldeman, R.A.A. & Tomlinson, P.B., 1978. Tropical trees and forests - an architectural analysis. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York. 441 pp.
[405]Hardjowasono, M.S., 1942. Gewicht en volume van verschillende vrucht- en zaadsoorten [Weight and volume of various fruits and seeds]. Korte Mededelingen No 20. Bosbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 172 pp.
[406]Harker, A.P., Sandels, A. & Burley, J., 1982. Calorific values for wood and bark and a bibliography for fuelwood. Report G 162. Tropical Products Institute, London. 20 pp.
[432]Hensleigh, T.E. & Holaway, B.K., 1988. Agroforestry species for the Philippines. AJA Printers, Malabon. 404 pp.
[436]Heyne, K., 1927. De nuttige planten van Nederlands-Indië [The useful plants of the Dutch East Indies]. 2nd edition, 3 volumes. Departement van Landbouw, Nijverheid en Handel in Nederlandsch-Indië. 1953 pp. (3rd edition, 1950. van Hoeve, 's-Gravenhage/Bandung. 1660 pp.).
[464]Ilic, J., 1990. The CSIRO macro key for hardwood identification. CSIRO, Highett. 125 pp.
[488]Japing, H.W. & Oey Djoen Seng, 1936. Cultuurproeven met wildhoutsoorten in Gadoengan - met overzicht van de literatuur betreffende deze soorten [Trial plantations of non teak wood species in Gadungan (East Java) - with survey of literature about these species]. Korte Mededeelingen No 55, part I to VI. Boschbouwproefstation, Buitenzorg. 270 pp.
[526]Kartasujana, I. & Martawijaya, A., 1979. Kayu perdagangan Indonesia - sifat dan kegunaannya [Commercial woods of Indonesia - their properties and uses]. Lembaga Penelitian Hasil Hutan, Bogor. 28 pp.
[536]Keating, W.G. & Bolza, E., 1982. Characteristics, properties and uses of timbers. Vol. 1. South-East Asia, northern Australia and the Pacific. Inkata Press Proprietary Ltd., Melbourne, Sydney & London. 362 pp.
[632]Kraemer, J.H., 1951. Trees of the western Pacific region. Tri-State Offset Company, Cincinnatti. 436 pp.
[633]Kramer, F., 1925. Kultuurproeven met industrie-, konstruktie- en luxe-houtsoorten [Investigations regarding the cultivation of different Javanese trees]. Mededeelingen No 12. Proefstation voor het Boschwezen, Buitenzorg. 99 pp.
[677]Lee, Y.H. & Chu, Y.P., 1965. The strength properties of Malayan timbers. Malayan Forester 28: 307-319.
[678]Lee, Y.H., Engku Abdul Rahman bin Chik & Chu, Y.P., 1979. The strength properties of some Malaysian timbers. Malaysian Forest Service Trade Leaflet No 34 (revised edition). Malaysian Timber Industry Board, Kuala Lumpur. 107 pp.
[696]Lemmens, R.H.M.J. & Wulijarni-Soetjipto, N. (Editors), 1991. Plant resources of South-East Asia No 3. Dye and tannin-producing plants. Pudoc, Wageningen. 195 pp.
[697]Letourneux, C., 1957. Tree planting practices in tropical Asia. FAO Forestry Development Paper No 11. FAO, Rome. 172 pp.
[736]Magini, E. & Tulstrup, N.P., 1955. Tree seed notes. I. Arid Areas II. Humid Tropics. FAO Forestry Development Paper 5. FAO, Rome. 354 pp.
[740]Malaysian Timber Industry Board, 1984. Peraturan pemeringkatan kayu keras gergaji Malaysia [The Malaysian grading rules for sawn hardwood timber]. Ministry of Primary Industries, Kuala Lumpur. 109 pp.
[741]Malaysian Timber Industry Board, 1986. 100 Malaysian timbers. Kuala Lumpur. x + 226 pp.
[780]Meniado, J.A. et al., 1975-1981. Wood identification handbook for Philippine timbers. 2 volumes. Government Printing Office, Manila. 370 pp. & 186 pp.
[804]Monsalud, M.R. & Tamolang, F.N., 1969. General information on Philippine hardwoods. Philippine Lumberman 15(7): 14-38.
[816]National Academy of Sciences, 1979. Tropical legumes. Resources for the future. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C. 331 pp.
[829]Ng, F.S.P., 1991-1992. Manual of forest fruits, seeds and seedlings. 2 volumes. Malayan Forest Record No 34. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 997 pp.
[831]Ng, F.S.P. & Mat Asri Ngah Sanah, 1991. Germination and seedling records. Research Pamphlet No 108. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 191 pp.
[839]Nielsen, I., 1985. The Malesian species of Acacia and Albizia (Leguminosae-Mimosoideae). Opera Botanica 81. 50 pp.
[857]Ntumbula, M., Ndiku, L., Tshisand, M. & Ntafu, M., 1990. Induced germination of Albizia lebbeck seeds inoculated with Rhizobium. Nitrogen Fixing Tree Research Reports 8: 116-117.
[861]Oey Djoen Seng, 1951. De soortelijke gewichten van Indonesische houtsoorten en hun betekenis voor de praktijk [Specific gravity of Indonesian woods and its significance for practical use]. Rapport No 46. Bosbouwproefstation, Bogor. 183 pp.
[865]Pader, L.P. & Chicano, D.S., 1993. Langil. RISE 5(1): 6-12.
[899]Pokhriyal, T.C. et al., 1990. Identification of some fast growing leguminous tree species for nitrogen fixation studies. Indian Forester 116: 504-507.
[910]Prinsen, J.H., 1986. Potential of Albizia lebbeck (Mimosaceae) as a tropical fodder tree; a review of literature. Tropical Grasslands 20(2): 78-83.
[933]Research Institute of Wood Industry, 1988. Identification, properties and uses of some Southeast Asian woods. Chinese Academy of Forestry, Wan Shou Shan, Beijing & International Tropical Timber Organization, Yokohama. 201 pp.
[934]Reyes, L.J., 1938. Philippine woods. Technical Bulletin No 7. Commonwealth of the Philippines, Department of Agriculture and Commerce. Bureau of Printing, Manila. 536 pp. + 88 plates.
[955]Rocafort, J.E., Floresca, A.R. & Siopongco, J.O., 1971. Fourth progress report on the specific gravity of Philippine woods. Philippine Architecture, Engineering & Construction Report 18(5): 17-27.
[970]Sadie, V.D. & Cornejo, A.T., 1990. Akle. RISE 2(7): 1-8.
[974]Salvosa, F.M., 1963. Lexicon of Philippine trees. Bulletin No 1. Forest Products Research Institute, College, Laguna. 136 pp.
[1038]Smitinand, T., 1980. Thai plant names. Royal Forest Department, Bangkok. 379 pp.
[1039]Smitinand, T. & Larsen, K. (Editors), 1970-. Flora of Thailand. The Forest Herbarium, Royal Forest Department, Bangkok.
[1086]Tamesis, F. & Aguilar, L., 1951. Important commercial timbers of the Philippines: their properties and uses. Popular Bulletin No 32. Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources. Bureau of Printing, Manila. 83 pp.
[1098]Timber Research and Development Association, 1979. Timbers of the world. Volume 1. Africa, S. America, Southern Asia, S.E. Asia. TRADA/The Construction Press, Lancaster. 463 pp.
[1104]Troup, R.S., 1921. Silviculture of Indian trees. 3 volumes. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
[1163]Verdcourt, B., 1979. A manual of New Guinea legumes. Botany Bulletin No 11. Office of Forests, Division of Botany, Lae. 645 pp.
[1177]von Meyenfeldt, C.F.W.M. et al., 1978. Restoration of devastated inland forests in South Vietnam. Volume III: List of tree species. Agricultural University, Wageningen. 219 pp.
[1198]Weidelt, H.J. (Editor), 1976. Manual of reforestation and erosion control for the Philippines. Schriftenreihe No 22. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Eschborn. 569 pp.
[1199]Werkgoep Tropische Houtteelt, 1973. Bebossing van geërodeerde gronden op Java - bijlage III: Houtsoorten [Afforestation of eroded lands in Java - Annex III: Tree species]. Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen. 128 pp.
[1221]Whitmore, T.C. & Ng, F.S.P. (Editors), 1972-1989. Tree flora of Malaya. A manual for foresters. 4 volumes. Malayan Forest Records No 26. Longman Malaysia Sdn. Berhad, Kuala Lumpur & Petaling Jaya.
[1242]Wong, T.M., 1982. A dictionary of Malaysian timbers. Malayan Forest Records No 30. Forest Research Institute Malaysia, Kepong. 259 pp.
Author(s)
J.P. Rojo
Albizia acle
Albizia carrii
Albizia chinensis
Albizia dolichadena
Albizia kostermansii
Albizia lebbeck
Albizia lebbekoides
Albizia papuensis
Albizia pedicellata
Albizia procera
Albizia retusa
Albizia rosulata
Albizia saponaria
Albizia splendens
Albizia carrii
Albizia chinensis
Albizia dolichadena
Albizia kostermansii
Albizia lebbeck
Albizia lebbekoides
Albizia papuensis
Albizia pedicellata
Albizia procera
Albizia retusa
Albizia rosulata
Albizia saponaria
Albizia splendens
Correct Citation of this Article
Rojo, J.P., 1998. Albizia Durazz.. In: Sosef, M.S.M., Hong, L.T. and Prawirohatmodjo, S. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 5(3): Timber trees; Lesser-known timbers. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea
Selection of Species
The following species in this genus are important in this commodity group and are treated separatedly in this database:
Albizia acle
Albizia carrii
Albizia chinensis
Albizia dolichadena
Albizia kostermansii
Albizia lebbeck
Albizia lebbekoides
Albizia papuensis
Albizia pedicellata
Albizia procera
Albizia retusa
Albizia rosulata
Albizia saponaria
Albizia splendens
Albizia acle
Albizia carrii
Albizia chinensis
Albizia dolichadena
Albizia kostermansii
Albizia lebbeck
Albizia lebbekoides
Albizia papuensis
Albizia pedicellata
Albizia procera
Albizia retusa
Albizia rosulata
Albizia saponaria
Albizia splendens

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.