Record Number
706
PROSEA Handbook Number
15(1): Cryptogams: Algae
Taxon
Acanthophora muscoides (L.) Bory
Protologue
In: Duperrey, Voy. monde, Crypt. 4: 156 (1828).
Family
RHODOMELACEAE
Chromosome Numbers
2n = unknown
Synonyms
Fucus muscoides L. (1753).
Vernacular Names
Philippines: culot (Ilocano).
Origin and Geographic Distribution
Acanthophora muscoides occurs throughout the tropics in the Atlantic Ocean (Caribbean, southern Atlantic Ocean), Indian Ocean (mainly in the western part), and Pacific Ocean (Japan, northern China, Taiwan, Melanesia). In South-East Asia it is found in northern Burma (Myanmar), Vietnam, Singapore, Indonesia (West Java), the Philippines and southern Papua New Guinea, and is always less frequent than Acanthophora spicifera (Vahl) Börgesen.
Uses
In the Philippines (Ilocos Norte) Acanthophora muscoides is hand-collected, dried and eaten cooked with other vegetables. In Thailand and Vietnam it has been listed as a potential economic alga.
Production and International Trade
No statistical data are available on the production of Acanthophora muscoides from the wild for food or medicinal uses.
Properties
In a project on plant growth hormonal activities, aqueous extracts from fresh samples of Acanthophora muscoides in the Philippines contain the highest auxin-like activity as well as the highest cytokinin-like activity of all seaweed extracts tested. Fresh samples of Acanthophora muscoides contain per g approximately: auxin 9500 µg, cytokinin 17 800 µg and gibberellin 165 µg. However, aqueous extracts of Acanthophora muscoides have not yet been directly tested in field bio-assays. Residues of petroleum-ether soluble fractions of methanolic extracts of this alga show rather high activity against mosquito larvae. The alga contains lambda carrageenan.
Description
Thalli erect, up to 60 mm tall, cartilaginous, reddish to purple, attached by a flat, discoid holdfast. Branching alternate, branches fleshy, terete, up to 1 mm in diameter, covered with spinous outgrowths. In cross-section axial cells small, rounded, 90 µm in diameter, surrounded by 5 periaxial cells; medulla distinct, 2—3 cells thick; cortex composed of 2 layers of very small rounded cells; epidermal cells elongated, fibre-like. Life cycle diplo-haplontic and isomorphic. Tetrasporangia borne in spinous stichidial ramuli. Gametophytes dioecious; cystocarps on short branchlets, sessile, ovate to urn-shaped; spermatangial clusters disciform.
Image
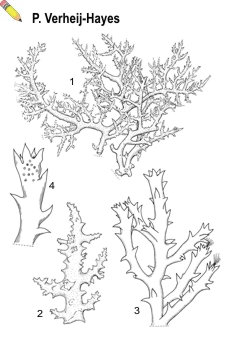 | Acanthophora muscoides (L.) Bory - 1, habit; 2, 3, details of vegetative apical parts; 4, apical part of sporophyte with tetrasporangia |
Ecology
Acanthophora muscoides occurs on reefs, attached to sandy-coral or rocky substrates protected from strong wave action.
Propagation and planting
Acanthophora muscoides is not known in phycoculture.
Harvesting
Acanthophora muscoides is only hand-collected from natural populations for direct local use.
Handling After Harvest
Acanthophora muscoides is sold and used fresh and/or sun-dried.
Prospects
Acanthophora muscoides has potential for the production of fine chemicals and medical products.
Literature
Cordero, P.A., 1977. Studies on Philippine marine red algae. Special Publication from the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, series IV. Seto, Wakayama Prefecture, Japan. 258 pp.
de Jong, Y.S.D.M., Hitipeuw, C. & Prud'homme van Reine, W.F., 1999. A taxonomic, phylogenetic and biogeographic study of the genus Acanthophora (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta). Blumea 44: 217—249.
Laserna, E.C., Veroy, R.L., Luistro, A.H. & Cajipe, G.J.B., 1981. Extracts from some red and brown seaweeds from the Philippines. Proceedings of the Xth International Seaweed Symposium, Göteborg, Sweden. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, Germany. pp. 443—448.
Montaño, N.E. & Tupas, L.M., 1990. Plant growth hormonal activities of aqueous extracts from Philippine seaweeds. SICEN (Seaweed Information Center) Leaflet 2: 1—5.
Prabha Devi, Solimabi, W., D'Souza, L. & Kamat, S.Y., 1997. Toxic effects of coastal and marine plant extracts on mosquito larvae. Botanica Marina 40: 533—535.
de Jong, Y.S.D.M., Hitipeuw, C. & Prud'homme van Reine, W.F., 1999. A taxonomic, phylogenetic and biogeographic study of the genus Acanthophora (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta). Blumea 44: 217—249.
Laserna, E.C., Veroy, R.L., Luistro, A.H. & Cajipe, G.J.B., 1981. Extracts from some red and brown seaweeds from the Philippines. Proceedings of the Xth International Seaweed Symposium, Göteborg, Sweden. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, Germany. pp. 443—448.
Montaño, N.E. & Tupas, L.M., 1990. Plant growth hormonal activities of aqueous extracts from Philippine seaweeds. SICEN (Seaweed Information Center) Leaflet 2: 1—5.
Prabha Devi, Solimabi, W., D'Souza, L. & Kamat, S.Y., 1997. Toxic effects of coastal and marine plant extracts on mosquito larvae. Botanica Marina 40: 533—535.
Author(s)
H.P. Calumpong
Correct Citation of this Article
Calumpong, H.P., 2001. Acanthophora muscoides (L.) Bory. In: Prud'homme van Reine, W.F. and Trono Jr, G.C. (Editors): Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 15(1): Cryptogams: Algae. PROSEA Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. Database record: prota4u.org/prosea

All texts are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Netherlands License
This license does not include the illustrations (Maps,drawings,pictures); these remain all under copyright.